Electric motor
In some operating modes of the electric drive, the electric motor performs the reverse energy conversion, that is, it operates in the mode of an electric generator.
By the type of created mechanical motion, electric motors are divided into rotating, linear, etc. By an electric motor, a rotating motor is most often meant, since it has received the greatest use.
The field of science and technology studying electrical machines is electromechanics. It is considered that its history begins in 1821 when the first electric motor was created by M. Faraday.
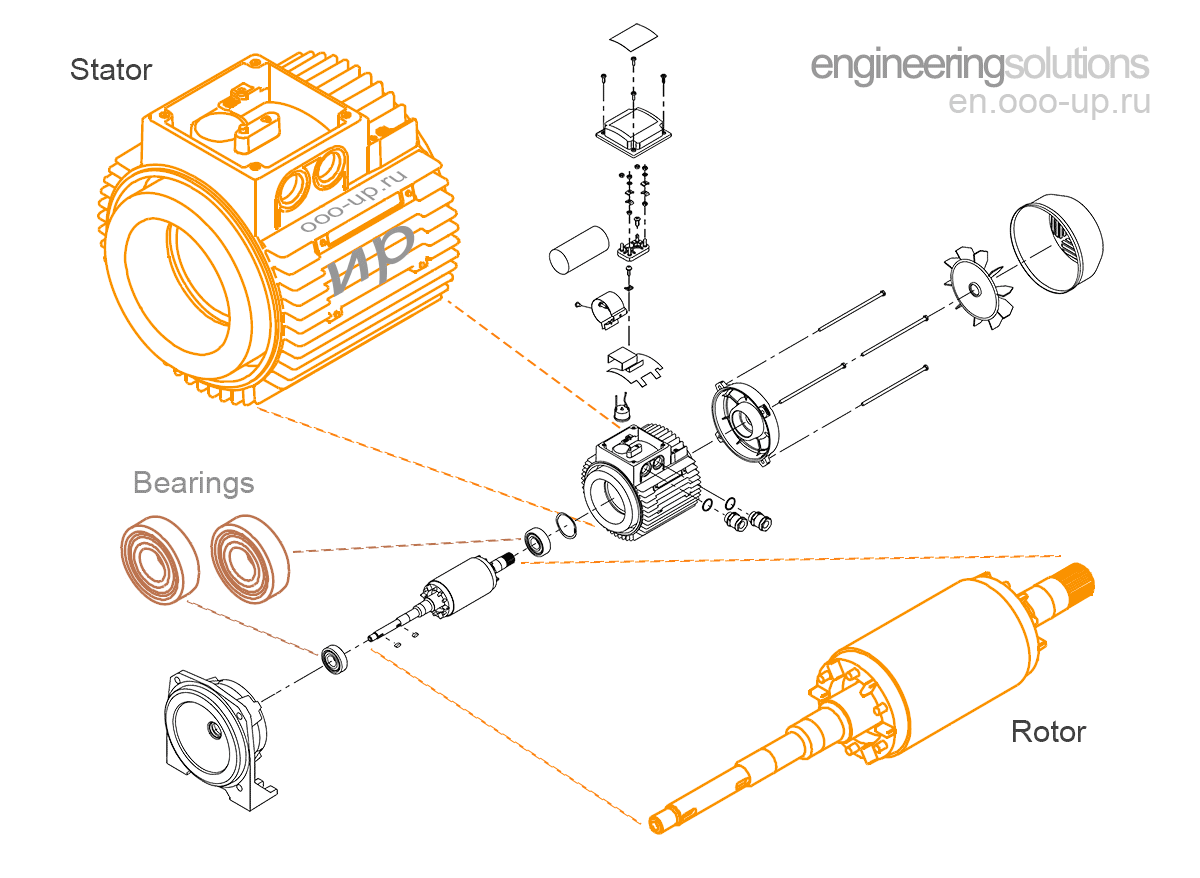
Motor construction
The main components of a rotating electric motor are the stator and the rotor. The stator is the fixed part. The rotor is the rotating part.
For most electric motors the rotor is located inside the stator. Electric motors in which the rotor is located outside the stator are called inside out electric motors.
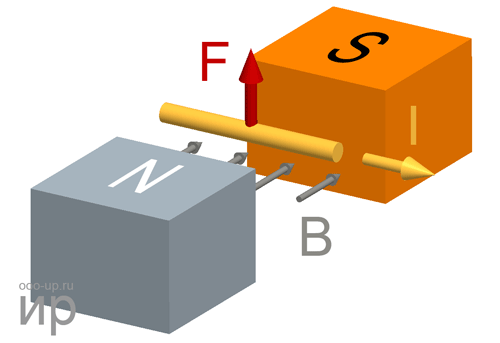
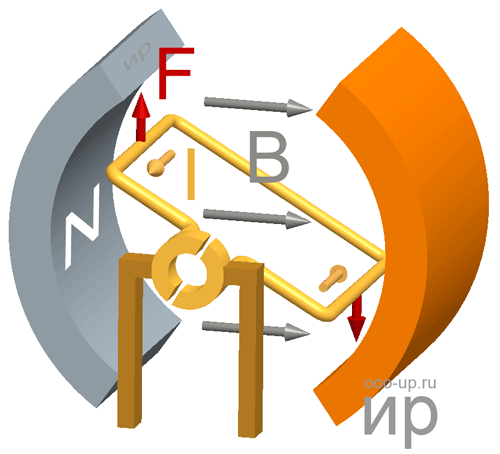
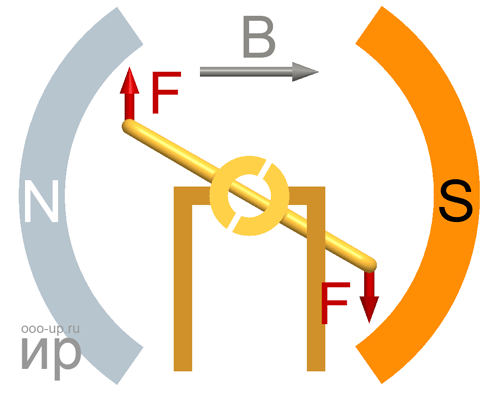
Working principle of the motor
- A detailed description of the working principle of electric motors of different types:
- Working principle of single-phase induction motor
- Working principle of a three-phase induction motor
- Working principle of a synchronous motor
Motor classification
| Rotating electric motor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Self-Commutated | Externally Commutated | |||
| Mechanical-Commutator Motors | Electronic-Commutator Motors1 | Induction motors | Synchronous motors | |
| AC | DC | AC2 | AC | |
|
|
|
|
|
| Simple electronics | Rectifier, transistors | More elaborate electronics |
Most elaborate electronics (VFD) when provided |
|
- This category does not represent a separate class of electric motors, since the devices in the category under consideration (BLDC, SRM) are a combination of a brushless motor, an electric converter (inverter) and, in some cases, a rotor position sensor (e.g. Hall sensors). In these devices, the electric converter, in view of its low complexity and small dimensions, is usually integrated into an electric motor.
- The electric motors used in BLDC and SRM are AC motors. However, due to the presence of an electric converter in these devices, they are connected to the DC power grid.
- A stepper motor is not a separate motor class. Structurally, it is the PMSM, SyRM or the hybrid SyRM-PM.
- DC - direct current
- BLDC - brushless DC
- EPC - electric power converter
- RPS - rotor position sensor
- SRM - switched reluctance motor
- SCIM - squirrel cage induction motor
- WRIM - wound rotor induction motor
- WRSM - wound rotor synchronous motor
- PMSM - permanent magnet synchronous motor
- SPMSM - surface permanent magnet synchronous motor
- IPMSM - interior permanent magnet synchronous motor
- SyRM – synchronous reluctance motor
- PM - permanent magnet
- VFD - variable frequency drive
Types of electric motors
Commutator motors
Сommutator machine is a rotating electrical machine, which has at least one of the windings involved in the main process of energy conversion, is connected to a collector [1]. In a collector motor, the brush-collector assembly performs the function of a rotor position sensor and a current switch in the windings.
Universal motor
Brushed DC electric motor
Commutatorless motors
Commutatorless electric motors can have contact rings with brushes, so do not confuse commutatorless electric motors and brushless electric motors.
A brushless machine is a rotating electrical machine in which all electrical connections of the windings involved in the basic process of energy conversion are carried out without sliding electrical contacts [1].
Induction motor
- Single phase
- Two phase
Synchronous motor
Special electric motors

Servomotor
The main parameters of the motor
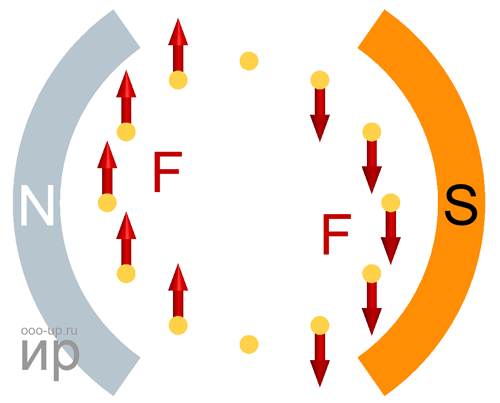
Motor torque
Torque (synonyms: a moment of force) is a vector physical quantity equal to the product of the radius-vector, drawn from the axis of rotation to the point of application of force, by the vector of this force.
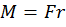 ,
,
- where M – torque, Nm,
- F – force, N,
- r – radius-vector, m
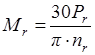 ,
,
- where Pr – rated motor power, W,
- nr - rated speed, min-1 [4]
The initial starting torque is the motor torque at start-up.
1 oz = 1/16 lb = 0,2780139 N
1 lb = 4,448222 N
torque is measured in ounce-force inch (oz∙in) or pound-force inch (lb∙in)
1 oz∙in = 0,007062 Nm
1 lb∙in = 0,112985 Nm
Motor power
Motor power is the useful mechanical power at the motor shaft.
Mechanical power
Power is a physical quantity that shows what kind of work the mechanism performs per unit of time.
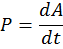 ,
,
- where P – power, W,
- A – work, J,
- t - time, s
Work is a scalar physical quantity equal to the product of the projection of the force on the direction F and the path s traversed by the point of application of force [2].
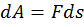 ,
,
- where s – displacement, m
For rotational motion
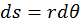 ,
,
- where
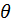 – angle, rad,
– angle, rad,
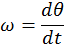 ,
,
- where
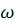 – angular velocity, rad/s,
– angular velocity, rad/s,
Thus it is possible to calculate the value of mechanical power on the shaft of a rotating electric motor.
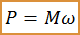
The energy conversion efficiency of the electric motor
Energy conversion efficiency of the electric motor is a characteristic of the machine effectiveness in relation to the conversion of electrical energy into mechanical energy.
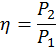 ,
,
- where
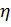 – efficiency of the electric motor,
– efficiency of the electric motor, - P1 - input power (electrical), Вт,
- P2 - useful output power (mechanical), W
- In this case, losses in electric motors are due to:
- electric losses - in the form of heat as a result of heating of conductors with the current;
- magnetic losses - core remagnetization losses: eddy current losses, hysteresis, and magnetic aftereffects;
- mechanical losses - friction losses in bearings, on ventilation, on brushes (if any);
- additional losses - losses caused by higher harmonics of magnetic fields arising due to the tooth structure of the stator, rotor and the presence of higher harmonics of the magnetomotive force of the windings.
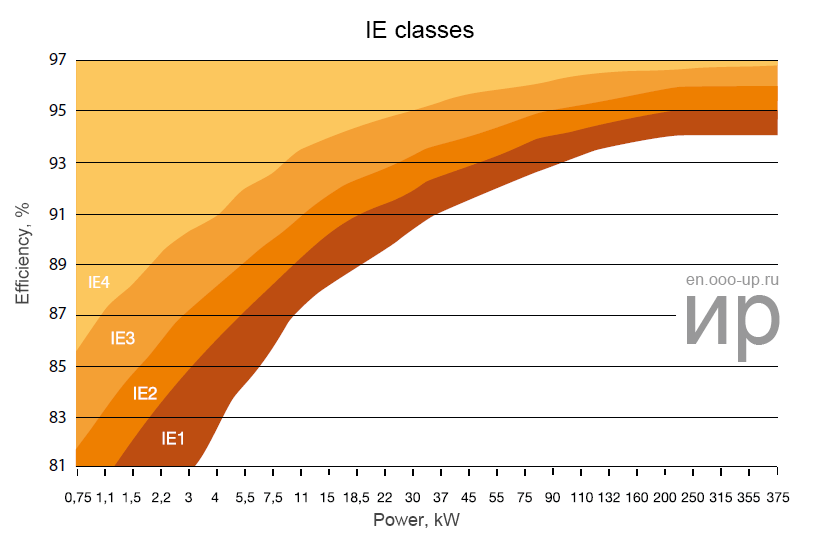
The efficiency of the electric motor can vary from 10 to 99% depending on the type and design.
The International Electrotechnical Commission determines the requirements for the efficiency of electric motors. According to the standard IEC 60034-31: 2010, four efficiency classes are defined for synchronous and induction electric motors: IE1, IE2, IE3, and IE4.
Rated speed
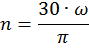 ,
,
- where n - is the rotation speed (frequency) of the electric motor, rev/min
Moment of inertia of the rotor
The moment of inertia - a scalar physical quantity, which is a measure of the inertia of a body in a rotational motion around an axis, is equal to the sum of the products of the masses of material points and the squares of their distances from the axis.
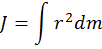 ,
,
- where J – the moment of inertia, kg∙m2,
- m - mass, kg
1 oz∙in∙s2 = 0,007062 kg∙m2
The moment of inertia is associated with the moment of force as follows
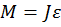 ,
,
- где
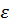 – angular acceleration, s-2 [2]
– angular acceleration, s-2 [2]
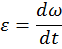 ,
,
Rated voltage
Rated voltage - is the voltage to which the power grid or equipment is designed and to which their characteristics is referred [3].
Electrical time constant
The electrical time constant is the time counted from the moment a DC voltage is applied to the electric motor, during which the current reaches a level of 63.21% (1-1/e) of its final value.
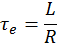 ,
,
- где
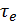 – time constant, s
– time constant, s
Torque-speed curve
The torque-speed curve (mechanical characteristic) of the motor is a graphically expressed dependence of the shaft speed from the electromagnetic torque at a DC supply voltage.
Comparison of characteristics of externally commutated motors
Below are the comparative characteristics of externally commutated electric motors, in terms of use as traction motors in vehicles.
-
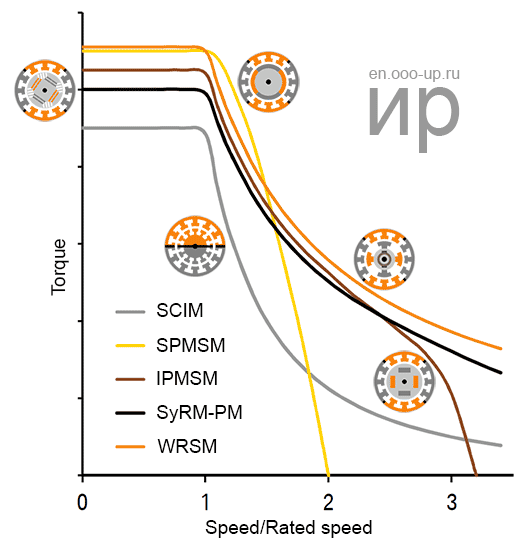
Comparison of torque-speed curves of different types of electric motors with a limited stator current
-
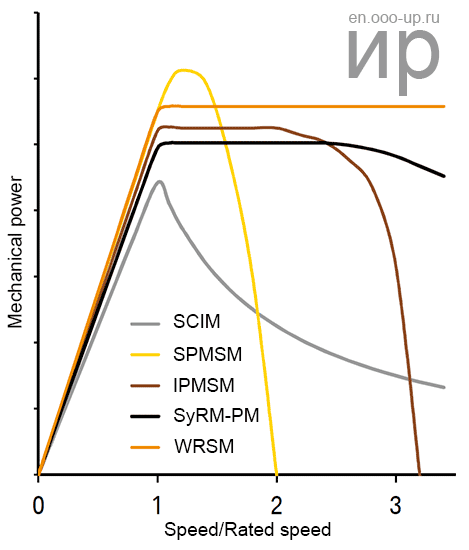
The dependence of power from the shaft rotation speed for motors of different types with a limited stator current
| Parameter |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constant power over speed range | |||||
| Torque per stator current | |||||
| Efficiency over complete operating range | |||||
| Weight |
- SyRM-PM - Permanent Magnet Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Motor (Hybrid Synchronous Motor)
- WRSM - Wound-Rotor Synchronous Motor
In accordance with the above indicators, a hybrid synchronous electric motor, namely a synchronous reluctance electric motor with incorporated permanent magnets, is most suitable for use as a traction electric motor in the automotive industry (the choice was made for the BMW i3 & BMW i8 concept). The use of reactive torque provides high power in the upper speed range. Moreover, such a motor provides very high efficiency in a wide operating range [7].
Electric motors applications
Electric motors are the largest consumers of electricity in the world, they account for about 45% of the total electricity consumed [6].
- Electric motors are used everywhere, the main applications:
- industry: pumps, fans, compressors, conveyors, driving force for other machines, etc.
- construction: pumps, fans, conveyors, elevators, heating, ventilation and air conditioning systems, etc.
- consumer devices: refrigerators, air conditioners, personal computers and laptops (hard drives, fans), vacuum cleaners, washing machines, mixers, etc.
| Motor | Functions | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Rotating electric motors | Pumps | Water supply and drainage systems |
| Heating, cooling and chilling systems, HVAC1, irrigation systems | ||
| Sewage system | ||
| Oil pipeline | ||
| Fans | Room air supply and exhaust, blowers, HVAC1 | |
| Compressors | Cooling machines for air conditioning and commercial freezers, refrigerators and freezers, HVAC1 | |
| Compressed-air storage and distribution system, pneumatic systems | ||
| Liquification systems | ||
| Rotating, mix, stir | Roller, rotors: metal, stone, plastics processing | |
| Extruder: aluminium, plastics processing | ||
| Textile handling: weaving, washing, drying | ||
| Mixers, stirring: food, colour, plastics | ||
| Transport | Passenger elevator, escalator, conveyor | |
| Goods elevator, cranes, hoists, conveyor | ||
| Vehicles: train, tram, trolley, cars, buses, electric cars, bikes and bicycles, cog wheel train, cable car, ropeway | ||
| Angular position (stepper motors, servomotors) |
Valve (open/close) | |
| Servo (setting position) | ||
| Linear motors | Open/close | Valve |
| Sort | Production | |
| Grab and place | Robots |
- HVAC - Heating, Ventilation, & Air Conditioning
Electric motor manufacturers
| A country | Manufacturer | Induction motor | Synchronous motor | Universal | Brushed DC motor | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCIM | WRIM | WRSM | PMSM, servo | SyRM, Hysteresis | Stepper | Wound field DC motor (wound stator) | PMDC motor (permanent magnet stator) | |||
| Switzerland | ABB Limited | |||||||||
| USA | Allied Motion Technologies Inc. | |||||||||
| USA | Ametek Inc. | |||||||||
| USA | Anaheim automation | |||||||||
| USA | Arc System Inc. | |||||||||
| Germany | Baumueller | |||||||||
| Slovenia | Domel | |||||||||
| USA | Emerson Electric Corporation | |||||||||
| USA | General Electric | |||||||||
| USA | Johnson Electric Holdings Limited | |||||||||
| Germany | Liebherr | |||||||||
| Switzerland | Maxon motor | |||||||||
| Japan | Nidec Corporation | |||||||||
| Germany | Nord | |||||||||
| USA | Regal Beloit Corporation | |||||||||
| Germany | Rexroth Bosch Group | |||||||||
| Germany | Siemens AG | |||||||||
| Brazil | WEG | |||||||||
- GOST 27471-87 Rotating electrical machines. Terms and definitions.
- I.V. Saveliev. The course of general physics, volume I. Mechanics, oscillations and waves, molecular physics.-Moscow: 1970.
- IEC 38-83 Standard voltages.
- GOST 16264.0-85 Low power electric motors.
- A.I.Voldek, V.V.Popov. Electrical machines. AC machines: A textbook for universities.- Saint Petersburg.: 2007.
- Paul Waide, Conrad U. Brunner. Energy-Efficiency Policy Opportunities for Electric Motor-Driven Systems. International Energy Agency Working Paper, Energy Efficiency Series.: Paris, 2011.
- Dr. J. Merwerth. The hybrid-synchronous machine of the new BMW i3 & i8 challenges with electric traction drives for vehicles. BMW Group, Workshop University Lund: Lund, 2014.